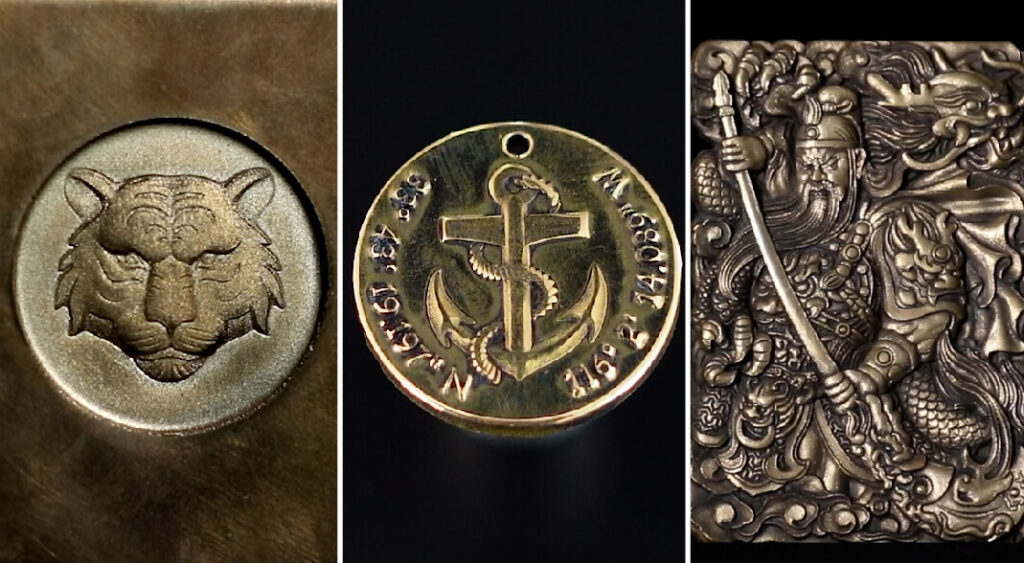
Laser technology has transformed manufacturing and creative industries. Both laser marking and laser engraving are widely used, yet they serve distinct purposes. Understanding the differences can help you choose the right technique for your projects.
What is Laser Marking?
Laser marking creates a permanent mark on a material’s surface without removing it. This process alters the surface color or texture, producing high-contrast and precise markings. Common methods include:
– Laser Annealing: Changes metal color via controlled oxidation.
– Laser Foaming: Produces foam-like textures on plastics.
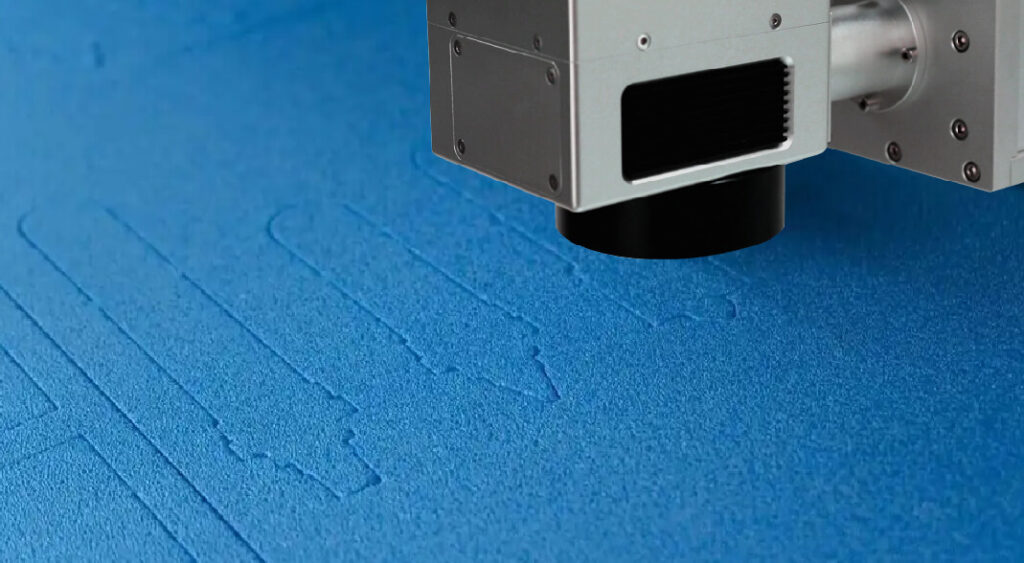

– Laser Carbon Migration: Brings carbon to the surface for dark marks.
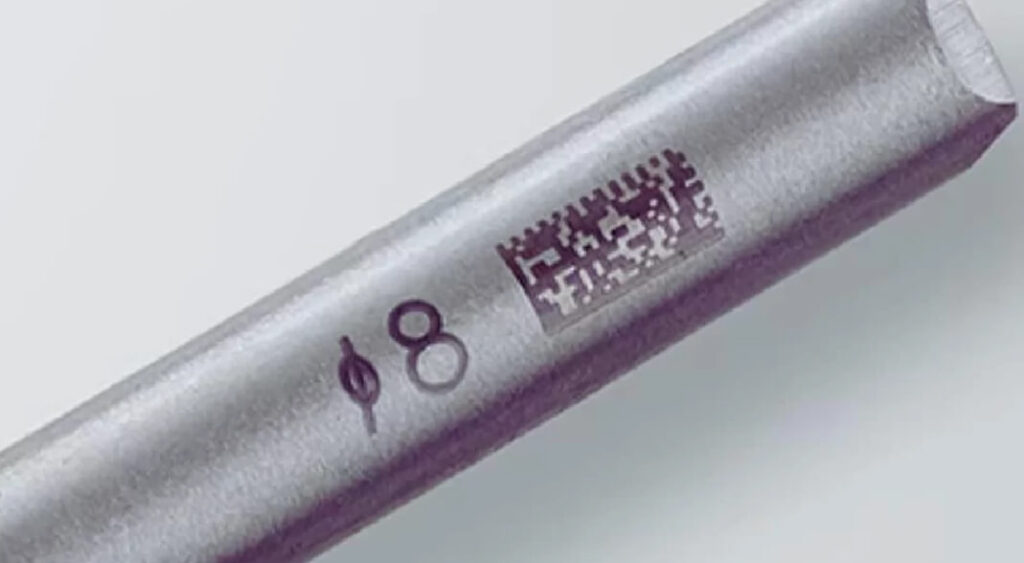

– Laser Coloration: Adjusts surface color on metals and plastics.
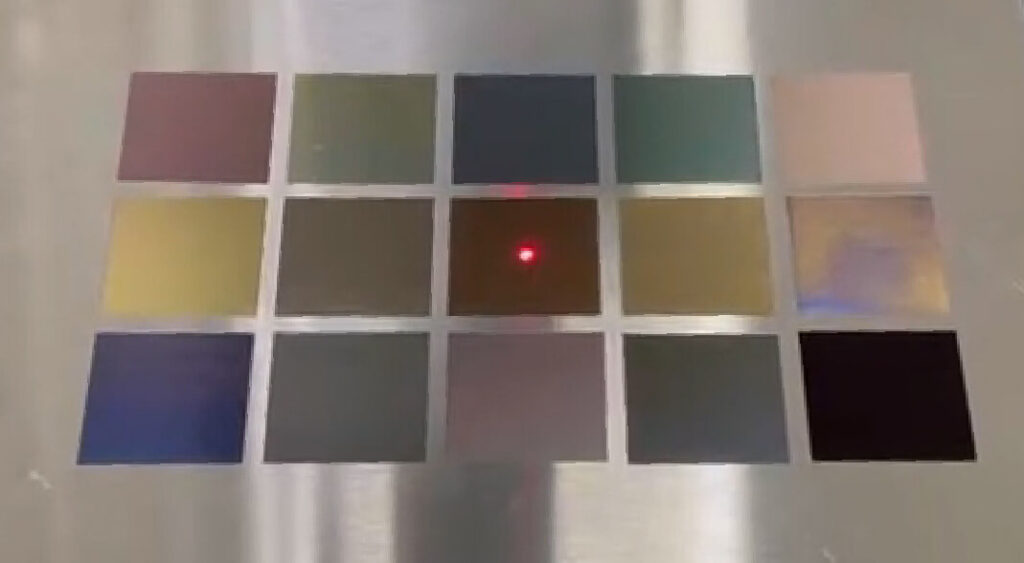

Laser marking is ideal for serial numbers, barcodes, QR codes, brand logos, and decorative designs on pens, jewelry, and nameplates. It is fast, energy-efficient, and suitable for high-volume production.
What is Laser Engraving?
Laser engraving removes material to create a deeper, tactile mark. The laser vaporizes the surface layer, and multiple passes can achieve greater depth. Engraving works on a variety of materials, including wood, metal, plastic, glass, and leather.
Applications include personalized gifts, trophies, logos, signage, and artistic patterns. Engraving is highly durable, suitable for items that require long-lasting identification or decorative effects.
Key Differences Between Laser Marking and Engraving
| Factor | Laser Marking | Laser Engraving |
| Process | Removing the surface material (discoloration or oxidation) | Removes material to create depth |
| Cut Depth | Surface-level, shallow | Typically 0.02 inches or deeper |
| Cost | Lower, faster and energy-efficient | Higher, slower process, more power |
| Material Compatibility | Metals, plastics, ceramics, glass | Most materials absorbing laser energy |
| Durability | Less durable, surface-only | Deep marks, long-lasting |
| Power Usage | Lower | Higher for deeper engraving |
Choosing Between Laser Marking and Engraving
When deciding, consider:
– Material Type: Reflective vs non-reflective materials absorb laser energy differently.
– Depth Requirement: Shallow marks for high-speed production, deep marks for durability.
– Project Scale: Laser marking is ideal for mass production; engraving suits custom items.
– Application: Regulatory labeling, branding, personalization, or artistic design.
Laser marking is perfect for traceability in automotive, medical, aerospace, and electronics industries. Laser engraving excels in customization, artistry, and creating tactile designs.
Applications
Laser Marking
– Industrial manufacturing: serial numbers, batch codes, component tracking.
– Medical instruments: forceps, implants, surgical tools.
– Electronics: circuit boards, small parts.
– Aerospace: turbine blades, bolts, landing systems.
– Jewelry & luxury goods: branding and anti-counterfeit markings.
– Packaging: expiration dates, QR codes, lot numbers.

Laser Engraving
– Personalization: gifts, trophies, jewelry.
– Signage & advertising: plaques, signs, logos.
– Art & design: sculptures, reliefs, wood/metal patterns.
– Electronics & medical: serial numbers, device identifiers.
– Aerospace & automotive: critical parts identification.
– Woodworking & crafts: intricate patterns, models, and custom objects.
Conclusion
Both laser marking and engraving are essential in modern industries. Laser marking is fast, cost-effective, and ideal for high-volume identification and branding. Laser engraving provides depth, tactile feel, and long-lasting results, perfect for customization and artistry. Choosing the right technique depends on your materials, production volume, and project goals.

