Laser Micromachining
WHAT IS LASER MICROMACHINING?
Laser micromachining, also known as “precision laser micromachining”, generally refers to a process with a processing size of several to hundreds of microns. It uses the high energy density (or brightness) and high directionality (extremely small divergence) of the laser to perform fine surface processing, engraving and cutting of all solid materials. Wherever the laser goes, the solid rapidly melts and vaporizes, leaving the surrounding material almost unaffected.
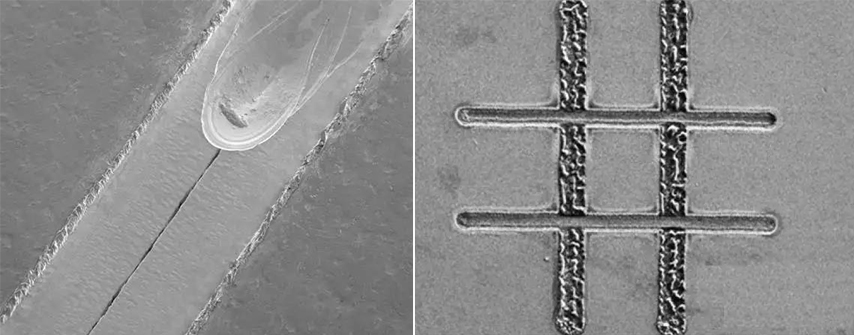
Advantages of Laser Micromachining
Comparing to traditional processing technology such as turning, wire cutting, stamping and chemical etching, laser micromachining have following advantages based on different applications:
1) Micro laser cutting can process any complex opening shape of metal and non-metal materials, easy for sampling and the cost is low; High precision (±0.01mm) and efficiency machining with small cutting seam width and slag hanging; high processing yield, generally not less than 98%.
2) Micro laser engraving is suitable for any graphics (serial number, QR code, logo and etc.) on metal and non-metallic materials.
3) Micro laser drilling can obtain small holes with a diameter of 30-40 μm (CO2 laser) in industry, or small holes of about 10 μm (UV laser),the minimum size of traditional mechanical drilling is 100 μm.
Laser Micromachining Applications
Laser micromachining covers a variety of applications, such as micro drilling, line ablation, scribing, cutting, field ablation, and block ablation and etc., usually with high requirements for accuracy, speed, and quality. Galvo scanning system, as a high-precision and high-speed servo control system, which is widely used in the field of micromachining and can be used to process various materials, such as ceramics, PCB boards, plastic films, semiconductors, metals, glass, sapphire, etc. For dynamic, non-standard shaped targets, the 3-axis scanning system can also identify the position of the target and process it.
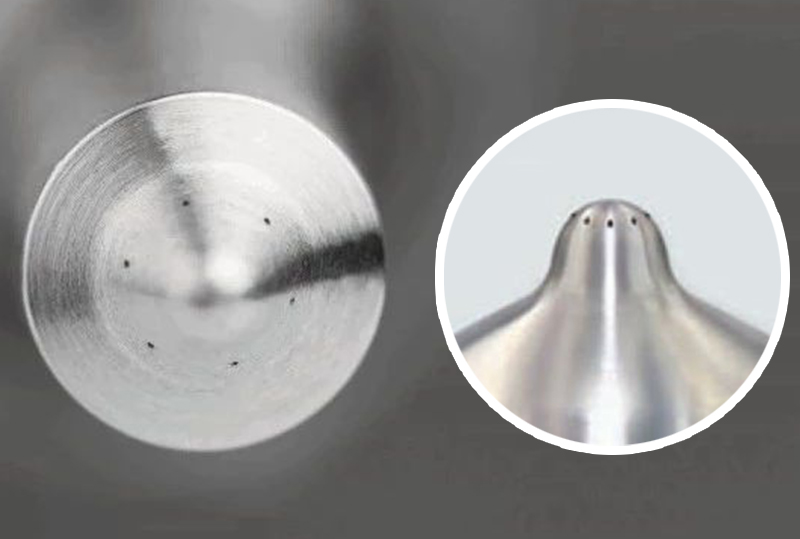

Micro drilling
- Drill hundreds of thousands of small holes with a diameter of 40100 μm on the circuit board or drill the mesh for filtering blood on the heart stent
(Requires a high-efficiency, high-precision galvanometer scanning system)
- Fuel injector

Micro scribing
Micro scribing is mainly used on metals and glass. The principle is that lines can be formed by superimposing laser pulses by scanning. Usually, a large number of scans can be used to penetrate deep into the ceramic until the depth of the lines reaches 1/6 of the thickness of the material. The individual modules are then separated from the ceramic substrate along these scribe lines.
Micro laser cutting
Micro laser cutting is the ablation of material with a laser, removing material until it is cut through. Usually used in sapphire, glass, metal film, PCB board. After setting the cutting range, the galvanometer can quickly and accurately repeat the processing according to the set range. For example, with the picosecond laser, it will not bring thermal influence to the surrounding materials.

Wire ablation (removal of plating)
Line ablation is the precise removal of a coating without damaging or slightly damaging the substrate material. Such as removing coatings from thin-film solar cell glass, or removing anti-corrosion coatings from automobiles in preparation for subsequent welding.

Surface structuring
Structuring can change the physical properties of the material surface, generally used in the fuel tank of the engine to create some microstructures that reduce wear, or structuring on the metal surface to achieve welding with plastics.
Micro laser engraving
Engraving is the creation of three-dimensional shapes by ablating materials, and is generally used to machine 3D shapes such as circular keyways. The 3-axis dynamic focus galvo system is suitable for such applications as it enables curved and stepped machining.
Laser Micromachining
WHAT IS LASER MICROMACHINING?
Laser micromachining, also known as “precision laser micromachining “, generally refers to a process with a processing size of several to hundreds of microns. It uses the high energy density (or brightness) and high directionality (extremely small divergence) of the laser to perform fine surface processing, engraving and cutting of all solid materials. Wherever the laser goes, the solid rapidly melts and vaporizes, leaving the surrounding material almost unaffected.

Advantages of Laser Micromachining
Comparing to traditional processing technology such as turning, wire cutting, stamping and chemical etching, laser micromachining have following advantages based on different applications:
1) Micro laser cutting can process any complex opening shape of metal and non-metal materials, easy for sampling and the cost is low; High precision (±0.01mm) and efficiency machining with small cutting seam width and slag hanging; high processing yield, generally not less than 98%.
2) Micro laser engraving is suitable for any graphics (serial number, QR code, logo and etc.) on metal and non-metallic materials.
3) Micro laser drilling can obtain small holes with a diameter of 30-40 μm (CO2 laser) in industry, or small holes of about 10 μm (UV laser),the minimum size of traditional mechanical drilling is 100 μm.
Laser Micromachining Applications
Laser micromachining covers a variety of applications, such as micro drilling, line ablation, scribing, cutting, field ablation, and block ablation and etc., usually with high requirements for accuracy, speed, and quality. Galvo scanning system, as a high-precision and high-speed servo control system, which is widely used in the field of micromachining and can be used to process various materials, such as ceramics, PCB boards, plastic films, semiconductors, metals, glass, sapphire, etc. For dynamic, non-standard shaped targets, the 3-axis scanning system can also identify the position of the target and process it.

Micro drilling
- Drill hundreds of thousands of small holes with a diameter of 40100 μm on the circuit board or drill the mesh for filtering blood on the heart stent
(Requires a high-efficiency, high-precision galvanometer scanning system)
- Fuel injector

Micro scribing
Micro scribing is mainly used on metals and glass. The principle is that lines can be formed by superimposing laser pulses by scanning. Usually, a large number of scans can be used to penetrate deep into the ceramic until the depth of the lines reaches 1/6 of the thickness of the material. The individual modules are then separated from the ceramic substrate along these scribe lines.

Micro laser cutting
Micro laser cutting is the ablation of material with a laser, removing material until it is cut through. Usually used in sapphire, glass, metal film, PCB board. After setting the cutting range, the galvanometer can quickly and accurately repeat the processing according to the set range. For example, with the picosecond laser, it will not bring thermal influence to the surrounding materials.

Wire ablation (removal of plating)
Line ablation is the precise removal of a coating without damaging or slightly damaging the substrate material. Such as removing coatings from thin-film solar cell glass, or removing anti-corrosion coatings from automobiles in preparation for subsequent welding.
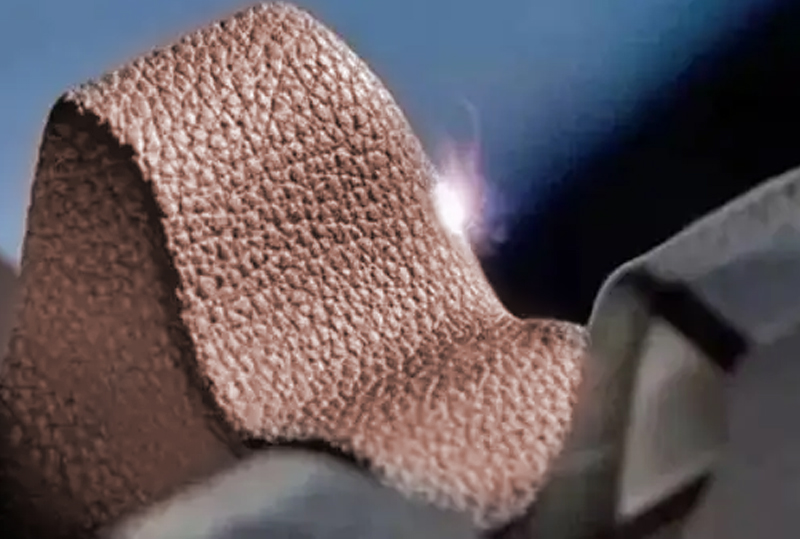

Surface structuring
Structuring can change the physical properties of the material surface, generally used in the fuel tank of the engine to create some microstructures that reduce wear, or structuring on the metal surface to achieve welding with plastics.

Micro laser engraving
Engraving is the creation of three-dimensional shapes by ablating materials, and is generally used to machine 3D shapes such as circular keyways. The 3-axis dynamic focus galvo system is suitable for such applications as it enables curved and stepped machining.



