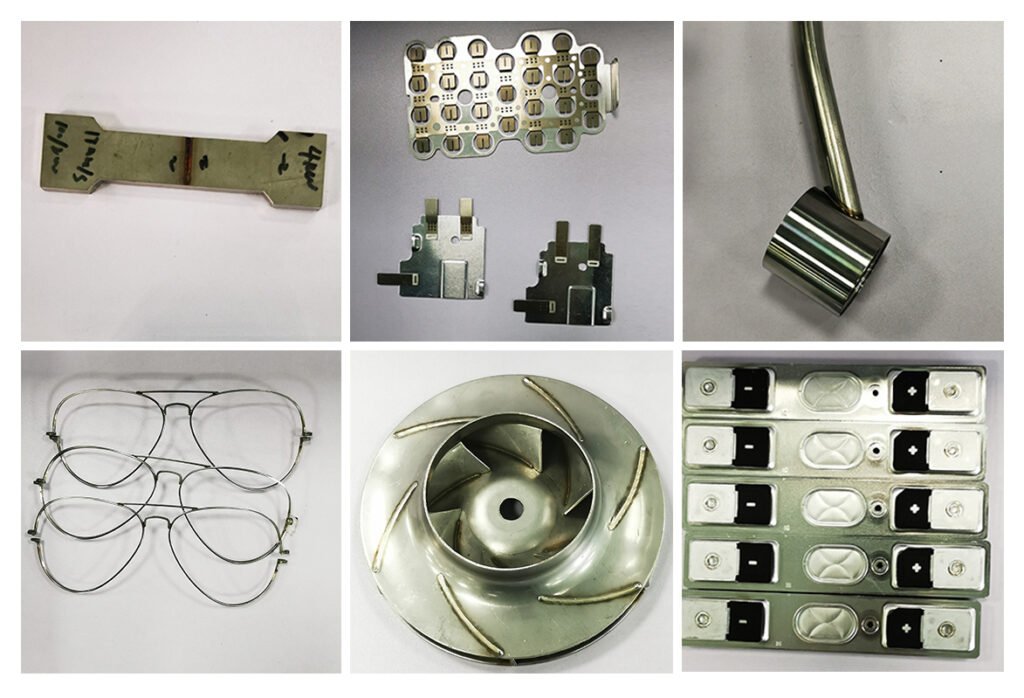
What is Laser welding
The Principle of laser welding
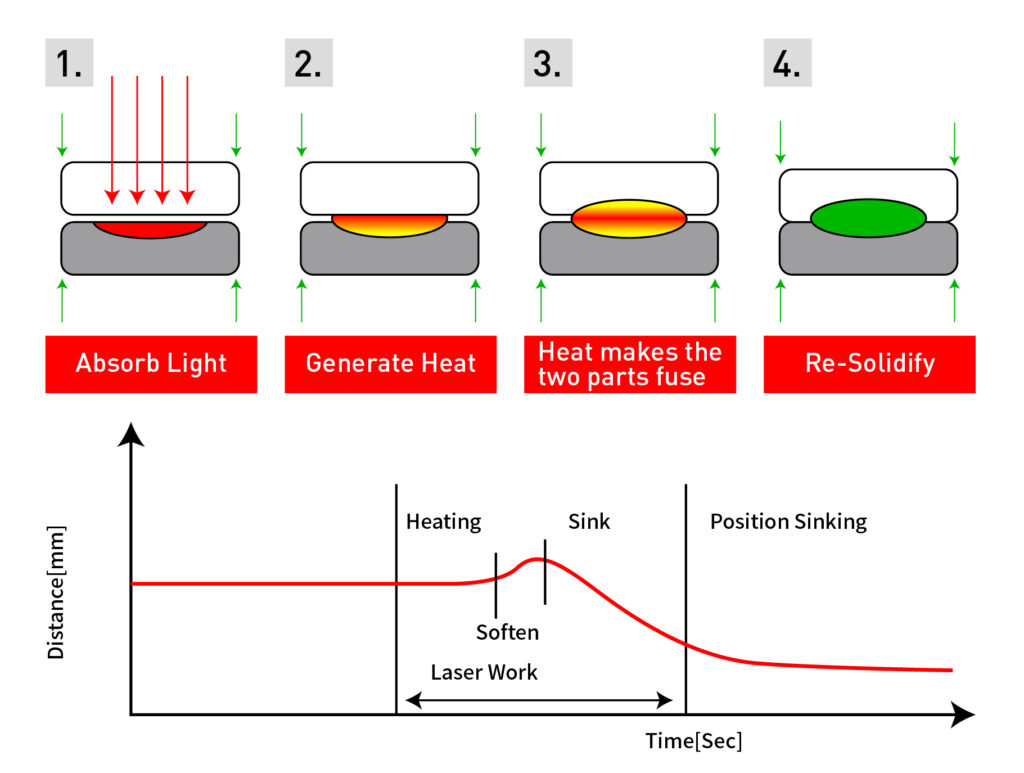
Laser welding belongs to fusion welding, and uses laser beam as welding heat source. The welding principle is: by a specific method to stimulate active medium, make it oscillate back and forth in the resonant cavity, and then convert it into a beam of stimulated radiation. When the beam and the workpiece contact each other, its energy is absorbed by the workpiece, and welding can be performed when the temperature reaches the melting point of the material.
According to the mechanism of welding molten pool formation, laser welding has two basic welding mechanisms: heat conduction welding and deep penetration (small hole) welding. The heat generated during heat conduction welding is diffused into the workpiece through heat transfer, so that the surface of the weld is melted without vaporization. It is often used in the welding of low-speed thin-walled components. Deep penetration welding vaporizes the material and forms a large amount of plasma. Due to the large heat, small holes will appear at the front of the molten pool. Deep penetration welding can completely penetrate the workpiece, and has large input energy and fast welding speed. It is the most widely used laser welding mode at present.
The advantages of laser welding
The main advantages of laser beam seaming compared to traditional arc welding processes are as follows:
- The laser beam quality is good, the focal spot diameter is small, and the welding spot can be generated without contacting the workpiece surface or applying force to the workpiece
- High strength combined with low welding volume: the welded workpiece can be subjected to bending or hydroforming
- Selective energy application in small area: reduce thermal stress and heat affected zone, extremely low distortion, suitable for precision sensitive parts
- High flexibility, can realize welding at any angle and various complex or irregular workpieces
- Applicable to a variety of heterogeneous metal materials, as well as titanium, nickel, zinc, copper and other metals and alloy materials
- Particularly suitable for automation technology, easy to integrate
- Good program control: machine tool control and sensor system detect process parameters and ensure quality
Laser welding applications
Compared with other commonly used welding techniques, laser welding technology produces almost no slag and debris, and does not require any adhesive to be added during the welding process, so the entire welding job can be completed in a clean room.
The application of laser welding in the field of medical equipment
Medical devices are usually hand-held tools or small components that are often used in surgery or implanted into the human body. The welds that connect these parts together are critical to patient health. Generally, the welding process with penetration depth and welding spot size less than 1mm is called laser micro welding. Laser micro-welding is commonly used for precision welding of products such as pacemakers, surgical blades, endoscopic instruments, and batteries. In addition, laser welding is widely used in shell packaging of active implantable medical devices, radiopaque marking of cardiac stents, ear wax protectors, balloon catheters, etc.
The application of laser welding on battery module
The cells of power batteries are usually made of “lighter” aluminum material, but also need to be made more “thin”. Generally, the shell, cover and bottom are basically required to be less than 1.0mm. At present, the thickness of the basic materials of mainstream manufacturers is 0.8mm. about. Laser welding is the only technology that can weld electroplated nickel to copper materials.
Its main advantages are as follows:
- Concentrated energy, high welding efficiency (more than 5 times higher than traditional welding speed), high processing precision, and large welding seam aspect ratio.
- Small heat input, small heat affected zone, small residual stress and deformation of the workpiece.
- The welding energy can be precisely controlled, the welding effect is stable, and the welding appearance is good; non-contact welding, optical fiber transmission, good accessibility and high degree of automation.
- When welding thin or fine-diameter wires, there is no problem of melt back like arc welding.
The Application of Laser Welding in the Automobile Industry
Laser welding is mainly used in laser group welding of body assemblies and sub-assemblies, laser tailor welding of unequal thickness plates and auto parts. Compared with the traditional full-mold forming manufacturing process, the production efficiency and accuracy are greatly improved.
Laser welding, compared with the traditional double-sided processing spot welding, greatly reduces the flange width, saving 40Kg of steel per vehicle, and increasing the strength of automotive components; laser tailor welding can combine different thicknesses, materials, strengths , stamping properties and several slabs with different surface treatment conditions are tailor-welded together to form a blank before stamping, and then pressed into the required coverings, such as side walls, bottom plates, inner door panels, pillars, etc. Its characteristics are to reduce the number of parts, reduce the weight of structural parts, and improve the quality and reliability of structural parts. Causes a non-uniformly distributed thermal stress that shapes the sheet. Its production cycle is short, the forming precision is high, and it is not limited to complex special-shaped parts.
Laser welding solutions
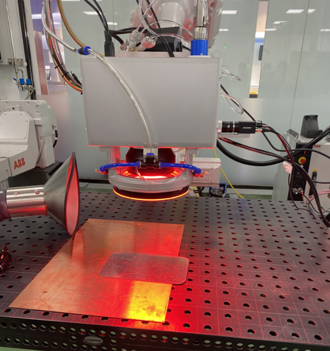
Sino-Galvo’s high-power laser galvanometers can be used for laser welding, 3D printing, laser cladding, laser quenching and other laser high temperature surface treatments. Laser galvanometer welding is to radiate a laser beam with high energy density to the metal surface. Under the interaction between the laser and the metal, the metal absorbs the laser energy and converts it into heat energy. After the metal melts, it cools and crystallizes to form a weld.
The welding speed range of high-power welding galvanometer can achieve more than 2000mm/s. When welding some complex trajectories such as triangle, circle, S shape, etc., it is not limited by the speed of the robot arm motor, and flexibly realizes high-speed welding of large-scale arbitrary curves in the plane. On the side plate welding of the module, the porosity of ordinary laser head welding is generally 20%~30%, while the porosity of galvanometer laser welding is less than 2%.
Compared with the traditional method, the high-power laser welding equipment replaces the two-dimensional worktable with a high-speed moving scanning lens, which greatly improves the welding speed and reduces the influence of the laser action on the material properties. Combined with professional software with powerful graphics processing function, program-controlled instantaneous multi-point welding is realized. And one scanning mirror group workstation can replace several traditional welding workstations.
What is Laser welding
The principle of laser welding
Laser welding belongs to fusion welding, and uses laser beam as welding heat source. The welding principle is: by a specific method to stimulate active medium, make it oscillate back and forth in the resonant cavity, and then convert it into a beam of stimulated radiation. When the beam and the workpiece contact each other, its energy is absorbed by the workpiece, and welding can be performed when the temperature reaches the melting point of the material.
According to the mechanism of welding molten pool formation, laser welding has two basic welding mechanisms: heat conduction welding and deep penetration (small hole) welding. The heat generated during heat conduction welding is diffused into the workpiece through heat transfer, so that the surface of the weld is melted without vaporization. It is often used in the welding of low-speed thin-walled components. Deep penetration welding vaporizes the material and forms a large amount of plasma. Due to the large heat, small holes will appear at the front of the molten pool. Deep penetration welding can completely penetrate the workpiece, and has large input energy and fast welding speed. It is the most widely used laser welding mode at present.
The advantages of laser welding
The main advantages of laser beam seaming compared to traditional arc welding processes are as follows:
- The laser beam quality is good, the focal spot diameter is small, and the welding spot can be generated without contacting the workpiece surface or applying force to the workpiece
- High strength combined with low welding volume: the welded workpiece can be subjected to bending or hydroforming
- Selective energy application in small area: reduce thermal stress and heat affected zone, extremely low distortion, suitable for precision sensitive parts
- High flexibility, can realize welding at any angle and various complex or irregular workpieces
- Applicable to a variety of heterogeneous metal materials, as well as titanium, nickel, zinc, copper and other metals and alloy materials
- Particularly suitable for automation technology, easy to integrate
- Good program control: machine tool control and sensor system detect process parameters and ensure quality
Laser welding applications
Compared with other commonly used welding techniques, laser welding technology produces almost no slag and debris, and does not require any adhesive to be added during the welding process, so the entire welding job can be completed in a clean room.
The application of laser welding in the field of medical equipment
Medical devices are usually hand-held tools or small components that are often used in surgery or implanted into the human body. The welds that connect these parts together are critical to patient health. Generally, the welding process with penetration depth and welding spot size less than 1mm is called laser micro welding. Laser micro-welding is commonly used for precision welding of products such as pacemakers, surgical blades, endoscopic instruments, and batteries. In addition, laser welding is widely used in shell packaging of active implantable medical devices, radiopaque marking of cardiac stents, ear wax protectors, balloon catheters, etc.
The application of laser welding on battery module
The cells of power batteries are usually made of “lighter” aluminum material, but also need to be made more “thin”. Generally, the shell, cover and bottom are basically required to be less than 1.0mm. At present, the thickness of the basic materials of mainstream manufacturers is 0.8mm. about. Laser welding is the only technology that can weld electroplated nickel to copper materials.
Its main advantages are as follows:
- Concentrated energy, high welding efficiency (more than 5 times higher than traditional welding speed), high processing precision, and large welding seam aspect ratio.
- Small heat input, small heat affected zone, small residual stress and deformation of the workpiece.
- The welding energy can be precisely controlled, the welding effect is stable, and the welding appearance is good; non-contact welding, optical fiber transmission, good accessibility and high degree of automation.
- When welding thin or fine-diameter wires, there is no problem of melt back like arc welding.
The Application of Laser Welding in the Automobile Industry
Laser welding is mainly used in laser group welding of body assemblies and sub-assemblies, laser tailor welding of unequal thickness plates and auto parts. Compared with the traditional full-mold forming manufacturing process, the production efficiency and accuracy are greatly improved.
Laser welding, compared with the traditional double-sided processing spot welding, greatly reduces the flange width, saving 40Kg of steel per vehicle, and increasing the strength of automotive components; laser tailor welding can combine different thicknesses, materials, strengths , stamping properties and several slabs with different surface treatment conditions are tailor-welded together to form a blank before stamping, and then pressed into the required coverings, such as side walls, bottom plates, inner door panels, pillars, etc. Its characteristics are to reduce the number of parts, reduce the weight of structural parts, and improve the quality and reliability of structural parts. Causes a non-uniformly distributed thermal stress that shapes the sheet. Its production cycle is short, the forming precision is high, and it is not limited to complex special-shaped parts.
Laser welding solutions
Sino-Galvo’s high-power laser galvanometers can be used for laser welding, 3D printing, laser cladding, laser quenching and other laser high temperature surface treatments. Laser galvanometer welding is to radiate a laser beam with high energy density to the metal surface. Under the interaction between the laser and the metal, the metal absorbs the laser energy and converts it into heat energy. After the metal melts, it cools and crystallizes to form a weld.
The welding speed range of high-power welding galvanometer can achieve more than 2000mm/s. When welding some complex trajectories such as triangle, circle, S shape, etc., it is not limited by the speed of the robot arm motor, and flexibly realizes high-speed welding of large-scale arbitrary curves in the plane. On the side plate welding of the module, the porosity of ordinary laser head welding is generally 20%~30%, while the porosity of galvanometer laser welding is less than 2%.
Compared with the traditional method, the high-power laser welding equipment replaces the two-dimensional worktable with a high-speed moving scanning lens, which greatly improves the welding speed and reduces the influence of the laser action on the material properties. Combined with professional software with powerful graphics processing function, program-controlled instantaneous multi-point welding is realized. And one scanning mirror group workstation can replace several traditional welding workstations.