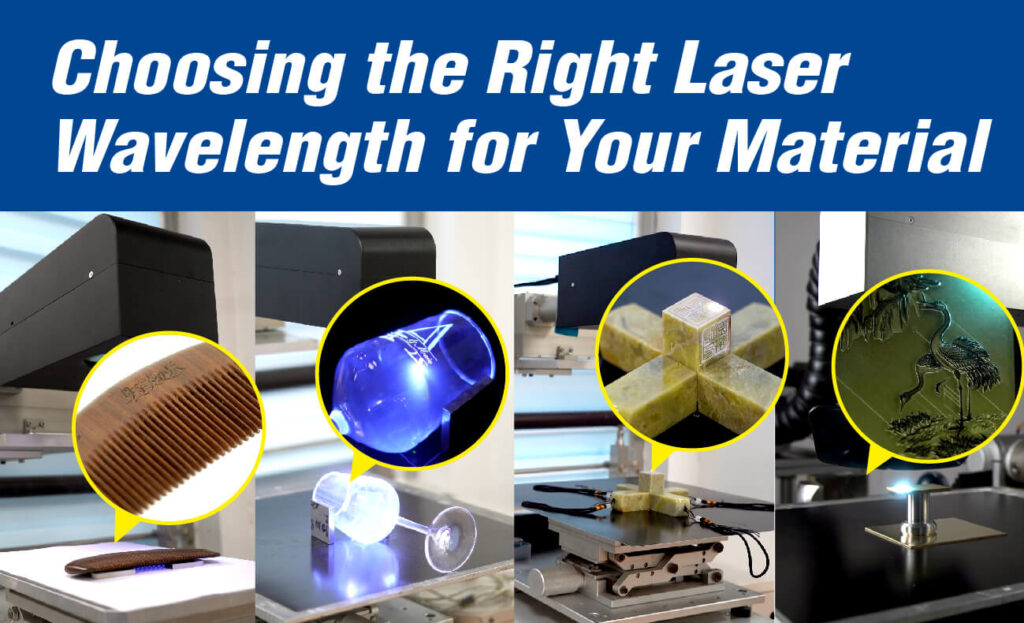
Choosing the appropriate laser wavelength for different materials is essential for achieving optimal laser processing results, whether for cutting, welding, marking, or engraving. Here’s a guide to selecting the right wavelength for various materials based on their specific characteristics.
Metals and the Ideal Laser Wavelength
Metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper, often reflect longer wavelengths such as the 10600 nm CO₂ laser. Shorter wavelengths, like the 1064 nm of fiber lasers, are more suitable due to their ability to be absorbed efficiently by metals. This is especially beneficial for metals with high reflectivity, such as aluminum and copper. Selecting the correct wavelength enhances precision and reduces energy waste in metal processing.
Plastics and CO₂ Laser Compatibility
Plastics generally absorb CO₂ laser (10600 nm) very well, making this wavelength ideal for cutting, engraving, and marking. However, certain plastics may also perform well with other wavelengths, such as 1064 nm or UV (355 nm). By choosing the appropriate laser for the plastic type, excessive heat buildup can be minimized, avoiding melting or burning and ensuring precise results.
Organic Materials and Laser Absorption
Organic materials, including wood, leather, and paper, absorb CO₂ laser (10600 nm) efficiently, which makes this wavelength ideal for engraving and cutting. Additionally, 1064 nm and 355 nm can also work well with organic materials when adjusted carefully to prevent over burning. Choosing the optimal wavelength ensures quality results, avoiding unnecessary damage to the material.
Glass and the Best Wavelength for Marking
Glass, particularly traditional glass, is transparent to longer wavelengths. As a result, UV lasers at 355 nm are more effective, as the shorter wavelength is readily absorbed by glass, allowing for precise marking. CO₂ lasers (10600 nm) may also be used with controlled settings, but the right wavelength—typically UV—is crucial for preventing cracks or shattering in glass applications.
Additional Tips for Choosing the Right Laser
- Material Absorption Characteristics: Investigate each material’s absorption spectrum to identify the most effective laser.
- Laser Type and Output: Consider the laser type as it can impact wavelength efficiency and material compatibility.
- Thickness of the Material: Thicker materials may require higher power, which can affect the selection of an appropriate wavelength.
- Application Requirements: Identify whether the goal is cutting, marking, or welding, as this will guide the choice of laser.
Laser Wavelength Suitability Table for Common Materials
| Material | 1064 nm (Fiber Laser) | 10600 nm (CO₂ Laser) | 355 nm (UV Laser) |
| Steel | ✔ | × | × |
| Aluminum | ✔ | × | × |
| Copper | ✔ | × | × |
| Acrylic (PMMA) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Polycarbonate | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| PVC | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Wood | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Leather | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Paper | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Glass | × | × | ✔ |
Summary
Selecting the correct laser wavelength for different materials maximizes efficiency, precision, and quality in laser processing applications. Factors such as absorption characteristics, laser type, material thickness, and processing goals all play crucial roles in identifying the optimal laser wavelength. If you have any questions about laser choosing or other questions, please feel free to contact us, we will have professionals to discuss with you.