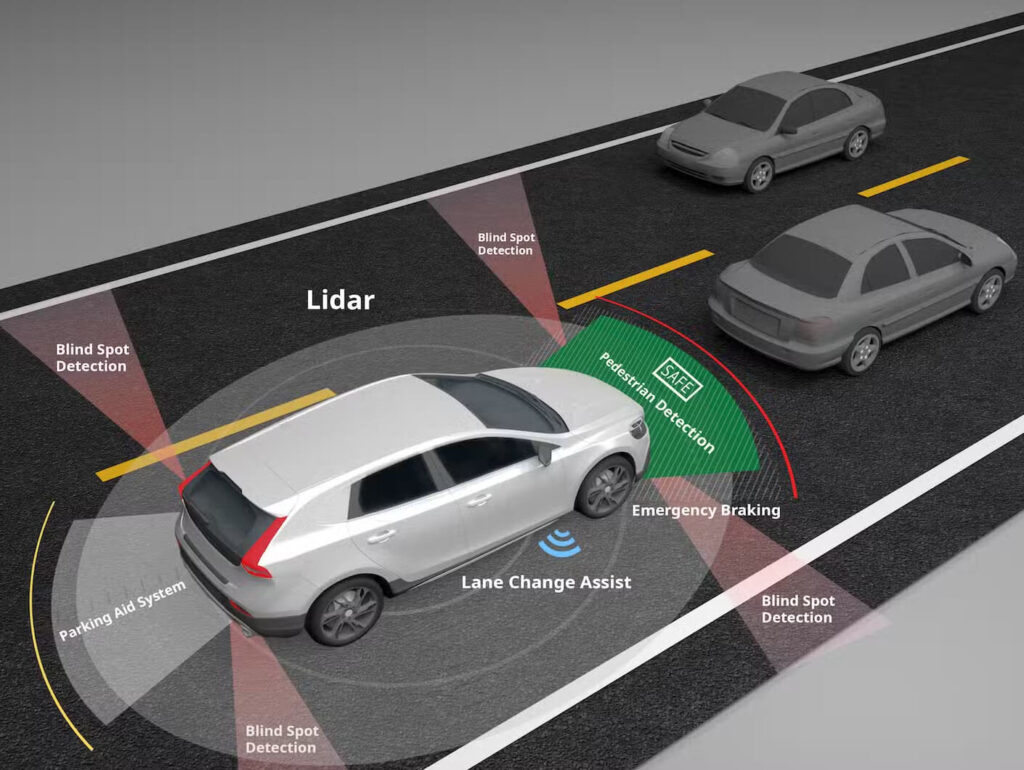
As autonomous driving technologies evolve, the role of LiDAR in ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) becomes increasingly critical. LiDAR offers accurate, real-time 3D mapping of the vehicle’s surroundings, enabling safe navigation, obstacle detection, and object tracking. A key component behind this capability is the galvo scanner, a precise optical mechanism responsible for controlling laser beam direction in LiDAR systems.
What is LiDAR in ADAS?
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing method that uses laser light to measure distances. In ADAS, LiDAR collects millions of data points per second, creating detailed 3D models of the road, nearby objects, vehicles, pedestrians, and more. These data are processed to support features such as adaptive cruise control, lane keeping, emergency braking, and semi-autonomous or fully autonomous driving.
The Critical Role of Galvo Scanners
A galvo scanner, short for galvanometer scanner, is an electro-optical device that controls the angle of a mirror to direct laser beams in a fast and precise manner. In the context of LiDAR in ADAS, galvo scanners allow the laser to sweep across a wide field of view, capturing rich spatial information with high resolution and accuracy.
- Precision Scanning
Galvo scanners provide ultra-fast and stable angular movement, allowing LiDAR systems to scan large environments with minimal motion blur. This is especially important when vehicles are moving at high speeds, as real-time environmental sensing is essential for quick decision-making.
- Flexible Field of View (FOV)
By adjusting the mirror’s angle, galvo scanners enable customizable scanning patterns. This flexibility supports both wide-angle scanning for general awareness and focused high-density scanning in critical zones, such as blind spots or pedestrian crossings.
- Compact and Scalable Design
Unlike bulky rotating mechanical systems, galvo-based LiDAR modules are smaller, lighter, and more suitable for vehicle integration. As automakers seek to embed sensors into bumpers, grilles, and windshields, galvo scanners offer an ideal solution for compact, high-performance systems.
- Improved Reliability Over Time
With fewer moving parts and well-established optical design principles, galvo-based LiDAR units tend to have greater durability and long-term performance stability compared to traditional mechanical rotating systems.
Galvo Scanners vs. MEMS in Automotive LiDAR
While both galvo and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) scanners are used in solid-state LiDAR, galvo scanners generally offer higher optical power handling and larger scanning angles. This makes them ideal for applications that demand longer-range detection and higher data accuracy — both crucial for ADAS safety standards.
Future Trends in LiDAR and ADAS Integration
As ADAS evolves toward full autonomy, LiDAR systems will need to deliver faster response times, higher resolution, and better environmental adaptability. Galvo scanners, especially those designed with automotive-grade standards, are poised to support this future by offering scalable performance, low latency, and seamless integration with AI-powered decision-making systems.
Conclusion
The use of LiDAR in ADAS is transforming how vehicles perceive and interact with their environment. At the heart of this revolution are galvo scanners, which enable accurate, responsive, and efficient laser beam steering. By empowering LiDAR systems with the ability to adaptively scan complex scenes, galvo scanners contribute directly to the safety, reliability, and intelligence of next-generation driving technologies.